First of all, before getting into knowing about MPFI (Multi-Point Fuel Injection) engine and CRDI(Common Rail Direct Injection) engine, please get to know the about the working of petrol and diesel engines.
The main purpose of an injection system is to supply properly metered fuel to the combustion chamber via intake valve/port.
MPFI Engine:
Multi Point Fuel Injection or Port injection system is used in petrol/gasoline engines (example – Maruti WagonR) in which each cylinder has a fuel-injector near the intake valve (Refer Image-I) and gets the name mulit-point based on the number of cylinders in the engine.
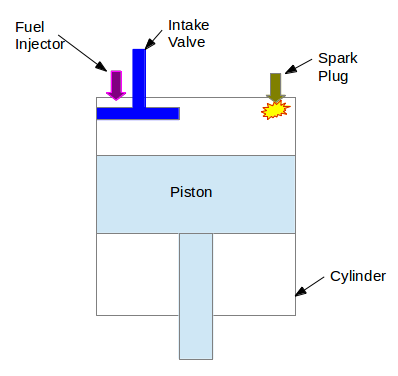
In simple terms, for the engine to produce power, proper amount of air-fuel mixture is required to be injected through the nozzle injector, which atomizes the fuel into tiny droplets into the combustion chamber, thereby spark plug ignites the mixture to propel the piston. MPFI came into play as a means to meet emission norms set by various countries and in addition it also helps in deriving out good vehicle performance and minimum quantity of fuel.
Before MPFI, petrol engines were using carburetor type engines (used in commuter type bikes), which have become obsolete now. MPFI is an advancement of carburetor technology but with an ECU in place.
In carburetor air-fuel mixture was a fixed ratio and hence right amount of fuel was metered resulting in excess burning of petrol resulting knocking/stalling and more pollutants to the atmosphere. But, MPFI with ECU which consists of many sensors acts as an intelligent system.
A few advantages of MPFI over carburetor is
1. Good engine response
2. Engine crank not necessary during cold start
3. Uniform air-fuel mixture and higher fuel efficiency.
These days, even 150cc powered engine bikes are equipped with fuel injectors for improving performance and fuel efficiency but with increase in cost.
Drawback of MPFI over carburetor is
1. Expensive to maintain in case of repairs.
2. Lower service intervals.
CRDI Engine:
CRDI – many must have come across seeing it behind cars boot and wondering what is it. Well, it’s Common Rail Direct Injection or sometimes referred as CRDe, TDIetc.
WHY CRDI?
Conventional non-CRDI (Mechanical indirect injection) engines are very sluggish and noisy to operate, in which the pump pressure forces the injectors to open to spray the fuel and hence abnormal spray patterns resulting in rich black smoke from the exhaust.
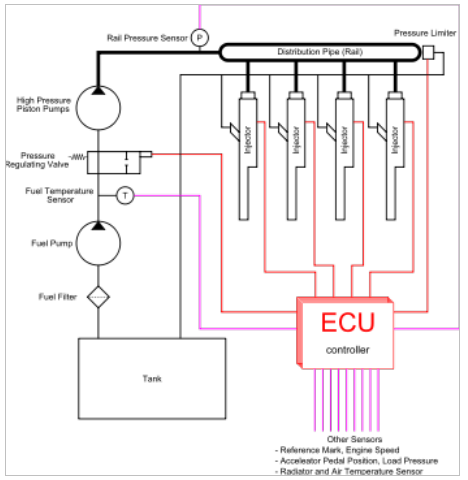
Image Source: Wiki
piston which helps build the pressure ranging from 1000bar to 3000 bar depending on the application. Fuel rail is an accumulator which stores the high pressure fuel and releases it to the injector nozzle based on inputs from ECU.
A major differentiating factor between MPFI and CRDI is that in CRDI the injector is placed directly over the piston and near the intake valve as in case of MPFI.
CRDI system is more complex when compared with MPFI, but yet is more efficient, offers more power and has good response to no or part engine loads which makes the diesel engine deliver more power even at low engine RPM.
A major drawback if I have to pinpoint one is if the distributor fuel rail fails, the engine comes to a grounding halt which is in turn overcome by a new technology in place called unit injectors, which intakes fuel from the high pressure fuel pump and has the distinct advantage of operating even when one or two unit injectors fail.
