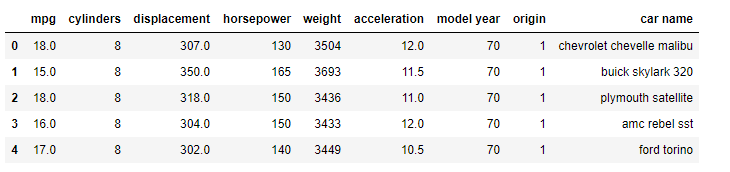
In this data science article we will use a dataset which has the following attributes:
1. mpg: continuous
2. cylinders: multi-valued discrete
3. displacement: continuous
4. horsepower: continuous
5. weight: continuous
6. acceleration: continuous
7. model year: multi-valued discrete
8. origin: multi-valued discrete
9. car name: string (unique for each instance)
We will see how to build a machine learning model to predict the first attributes (mpg) given the rest.
So, let’s get started.
If you don’t already have python installed, please install it. I shall be using the Anaconda distribution of Python through Jupyter notebook.
# starting with Importing all the neccessory functions from Scikit Learn
import numpy as np
import pandas as pd
from sklearn.linear_model import LinearRegression
from sklearn.model_selection import train_test_split
from sklearn.preprocessing import PolynomialFeatures
I have copied the data set and saved it in the carMillage.csv file.
#importing the dataset from the CSV file
df=pd.read_csv(‘carMillage.csv’)
# lets check the dataset
df.head()
Next, I am splitting the dataset into two: df1 for training and testing. df2 for predicting. Also dropping the last three columns from our dataset:
df1=df.iloc[:-3,:-3]
df2=df.tail(3).iloc[:,:-3]
Removing unwanted charecters in the horsepower column:
df1 = df1[~df1[‘horsepower’].isin([‘?’])]
Converting all the data to Float:
df1=df1.astype(float)
Taking the first column (mpg) as target:
y=df1.iloc[:,0:1]
Selecting rest of the column as features:
X=df1.iloc[:,1:]
#Creating a second order polynomial feature
poly = PolynomialFeatures(degree=2)
#Converting our input linear dataset to the polynomial dataset
X_poly = poly.fit_transform(X)
#Splitting the input data into test and train dataset
X_train, X_test, y_train, y_test=train_test_split(X_poly,y,random_state=0)
#Fitting the train data
linreg_poly=LinearRegression().fit(X_train,y_train)
Calculating the overall score of the model:
linreg_poly.score(X_test,y_test)
0.7791033345522557
Lets see the df2, to be used for prediction:
mpg cylinders displacement horsepower weight acceleration
395 32.0 4 135.0 84 2295 11.6
396 28.0 4 120.0 79 2625 18.6
397 31.0 4 119.0 82 2720 19.4
Selecting the second row of df2 for prediction:
test=np.asarray(df2.iloc[1,1:])
test=test.reshape(1,-1)
test
array([4, 120.0, '79', 2625, 18.6], dtype=object)
Lets put the selected row (test) as input to our model:
linreg_poly.predict(poly.fit_transform(test))
and the output we got:
array([[27.13930186]])
against the actual value of 28