Normally the Carbon dioxide (CO2 laser is used here for precision cutting of materials. CO2 laser is typically produced by passing a current into the DC –excited gas mix. The laser beam is then directed and controlled by computer to cut the work piece.
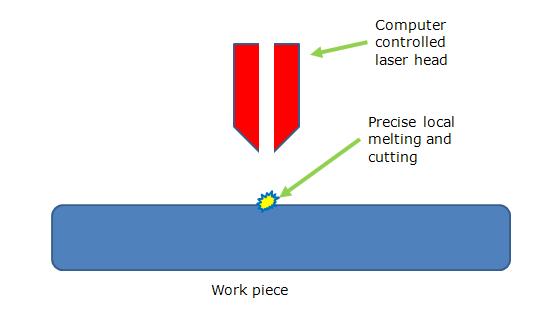
Level of surface finish achieved: 6.3-0.20 micro meters
Advantages:
– Very fast rate of operation
– Narrow heat affected zone
– Complicated profile can be cut
– Very hard brittle materials can be cut
Disadvantages:
– Costly equipment
– Maximum thickness that laser can cut is 6mm for plain carbon steel
Ideal applications: the laser cutting can be applied for boring, cutting, engraving variety of materials including stainless steel, mild steel, aluminum, titanium, epoxy, plywood, copper.
