Have you ever wondered how the stuffs like engine works of your car to keep you moving? Most of the cars you see on the road are run either by petrol or by a diesel internal combustion (IC) engine. The working of a petrol engine is little different than how does a diesel car engine works. So, before going to the working of the IC engine, I will first introduce the difference between diesel and the petrol IC engine.
Diesel Engine vs Petrol or Gasoline Engine
- Ignition process: The ignition of the petrol engine is occurred by a battery powered spark plug; however, for the diesel engine the heat generated by the compression process of the air is sufficient to ignite the air fuel mixture. Technically, the ignition of a gasoline engine is governed by otto cycle and that of a diesel engine is diesel cycle.
- Fuel efficiency: Due to the higher compression ratio, the diesel engine has a better fuel efficiency than it petrol counterpart.
- Turbo charging: For diesel engine, fuel is sprayed in the combustion chamber directly when the piston reached almost at the top, so there is no pre-mixing of air and fuel for diesel engine. But for petrol engine, air fuel is mixed before and then introduced in combustion chamber. So, higher level of turbo-charging is not possible for petrol engine because it may pre-ignite in that case.
- Engine weight: To support higher level of compression, diesel engines require heavy construction, thus diesel engines are heavier than gasoline IC engine of same power.
What is a Four Stroke Engine?
The each upward or downward movement of the piston is counted as one stroke. A four stroke engine completes one combustion cycle with four strokes (two downward strokes and two upward strokes). The combustion cycle starts with the entry of air (or air fuel mixture) to the cylinder and ends with the realizing of the exhaust gas from the cylinder. The four strokes are: intake stroke, compression stroke, combustion or power stroke, exhaust stroke.
How Does a Four Stroke Diesel Internal Combustion Engine Works?
- Intake stroke

– The piston starts going downward.
– The inlet valve opens up.
– Compressed air (turbocharged) get into the cylinder.
– The stroke ends when piston reached at the extreme bottom of the cylinder (BDC).
– The outlet valve and fuel injector remains closed.
- Compression stroke
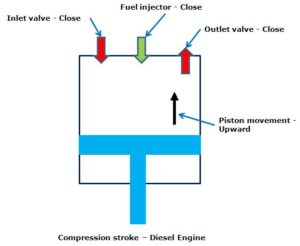
– After the piston reached BDC, it starts moving upward.
– The inlet, outlet and fuel injector valves remain closed.
– The upward piston movement compresses the sucked air in the cylinder.
– The stroke ends when the piston reaches the extreme top of the cylinder (TDC).
- Combustion or Power Stroke
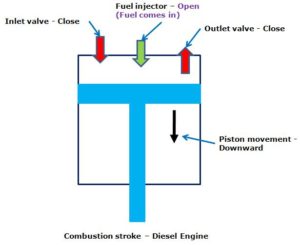
– At the end of the previous stroke or at the beginning of this stroke, the fuel injector valve opened up and fuel is sprayed into the cylinder.
– Ignition starts and the expansion of the gas generate power to push the piston downward. The power causes the crank shaft to rotate.
– The inlet and exhaust valves remain closed.
– This stroke ends when the piston reaches to the BDC.
- Exhaust Stroke

– The piston starts going upward.
– The inlet valve and the fuel injector valve remain closed.
– The outlet valve is opened up.
– The upward piston movement forces the exhaust gas leave the cylinder through the outlet valve.
How Does a Four Stroke Petrol Internal Combustion Engine Works?
- Intake stroke

– The piston starts going downward.
– The inlet valve opens up.
– The air fuel mixtures get into the cylinder.
– The stroke ends when piston reached at the extreme bottom of the cylinder (BDC).
– The outlet valve remains closed and the spark plug remains off.
- Compression Stroke

– After the piston reached BDC, it starts moving upward.
– The inlet, outlet valves remain closed.
– The spark plug remains off.
– The upward piston movement compresses the sucked air in the cylinder.
– The stroke ends when the piston reaches the extreme top of the cylinder (TDC).
- Combustion Stroke or Power Stroke

– At the end of the previous stroke or at the beginning of this stroke, the spark plug produces spark into the air fuel mixture of the cylinder.
– Ignition starts and the expansion of the gas generate power to push the piston downward. The power causes the crank shaft to rotate.
– The inlet and exhaust valves remain closed.
– This stroke ends when the piston reaches to the BDC.
- Exhaust Stroke
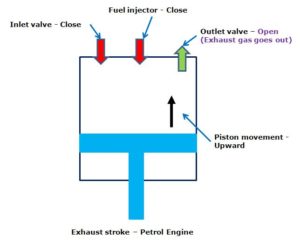
– The piston starts going upward.
– The inlet valve and remain closed.
– The spark plug remains off.
– The outlet valve is opened up.
– The upward piston movement forces the exhaust gas leave the cylinder through the outlet valve.
While explaining the working of a typical car engine and difference between the petrol and diesel IC engines, it has been taken care to not to use the technical terms like thermodynamic cycles and engine torque curves to keep the article simple. If you feel i have oversimplified the article or missed something, please drop a comment.
Hi, I am Shibashis, a blogger by passion and an engineer by profession. I have written most of the articles for mechGuru.com. For more than a decades i am closely associated with the engineering design/manufacturing simulation technologies. I am a self taught code hobbyist, presently in love with Python (Open CV / ML / Data Science /AWS -3000+ lines, 400+ hrs. )

Great job breaking down each segment of the combustion cycle. In generality, I knew how the engine worked but I never took the time to visualize the event. This really helped me understand the cycles through the pictures and your ability to break down the steps so they can be easily read and followed. Keep it up!
Tim Carlstedt
CPM Industries
http://www.cpm-industries.com
How turbocharger works?Explain.